CBPF Participates in the Open Conference on the Topic: "National Policy for Scientific Instrumentation" Organized by SBF
The Brazilian Society of Physics (SBF) organized an OPEN CONFERENCE - STRUCTURING AXIS III OF ENCTI, on "National Policy for Scientific Instrumentation for Innovative Science and Technology" as part of the 5th National Conference on S&T&I - FOR A FAIR, SUSTAINABLE, AND DEVELOPED BRAZIL. Dr. Marcelo Portes de Albuquerque, Coordinator of Technological Development, NIT-Rio and the Laboratory of Computing and Artificial Intelligence (LITCOMP-IA) at the Brazilian Center for Physics Research (CBPF), provided a comprehensive overview of the concept of scientific instrumentation and its relationship with CBPF.
THE IMPORTANCE OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTATION IN ADVANCING INNOVATIVE RESEARCH
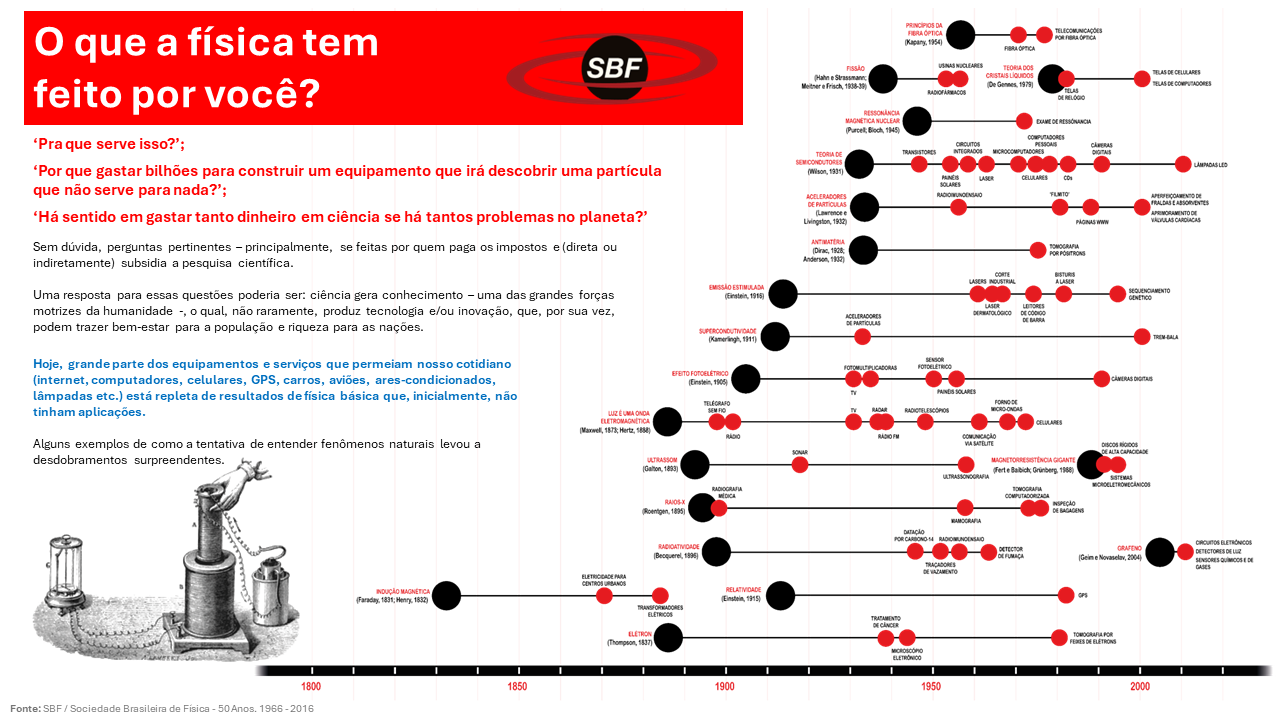
In Dr. Marcelo's presentation, he offered an overview of the concept of scientific instrumentation, understood as the development and use of devices or systems necessary for the observation, measurement, and analysis of scientific phenomena. During the introduction, he addressed a common misconception that limits the general public's understanding of the term "instrumentation" to medical applications, such as scalpels and other surgical instruments. However, scientific instrumentation includes a much broader range of tools and technologies designed to advance scientific knowledge through precise data and detailed observations. The presentation also emphasized the role of scientific instrumentation in promoting innovative research. Examples of instrumentation devices, including telescopes and spectrometers, were presented to demonstrate how such tools contribute to significant discoveries and broaden our understanding of the universe. The effectiveness of scientific instrumentation is directly related to its ability to enable the exploration and understanding of phenomena previously inaccessible to science.

THE SYNERGY BETWEEN PHYSICS AND SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTATION
In the second part of the presentation, Dr. Marcelo addressed the relationship between physics and scientific instrumentation, explaining how both are fundamental to Brazil's academic and industrial development. He highlighted how these areas are intertwined, facilitating technological advancement and innovation in various sectors. Dr. Marcelo also spoke about the continuous investment in new equipment and technologies, which enable physics research and contribute to expanding the country's scientific horizon. Specific examples, such as the evolution of multi-user laboratories and collaboration with the private sector, were used to demonstrate the importance of scientific instrumentation in developing a robust research and development infrastructure.
Dr. Marcelo also highlighted CBPF's role in developing scientific instrumentation and its contribution to national innovation capacity through its programs and projects. He mentioned the importance of the Professional Master's Degree in Scientific Instrumentation, which has been essential in training qualified professionals and promoting innovations. Additionally, he detailed the activities of the Technological Innovation Center (NIT-Rio) in protecting developed innovations and facilitating technology transfer between CBPF and the productive sector. The structure and benefits of Multi-User Laboratories were explained, highlighting how these spaces promote collaboration and the sharing of high-tech resources among different research groups.
CONCLUSION:
The Essentiality of Scientific Instrumentation and Support for R&D
Concluding his presentation, Dr. Marcelo reaffirmed the essentiality of scientific instrumentation for Brazil's scientific and technological progress. He highlighted the need for continuous support and investment in research and development (R&D) to maintain and expand instrumentation capabilities, aiming not only at scientific advancements but also at the practical application of these advancements for society's benefit.
Cycle of Science, Technology, and Innovation (S&T&I)
Dr. Marcelo also concluded by recognizing that the Cycle of Science, Technology, and Innovation (S&T&I) is divided into six main phases, each representing a stage of development from initial research to the eventual renewal or decline of a technology or application. These cycles exist and must be monitored. The precursor phase involves observing scientific phenomena, stimulating industrial interest and investment, where the first demonstration of applied science potential occurs. The embryonic phase focuses on improving the reliability and performance of technology until its field demonstration. The nurturing phase emphasizes improving the price and performance of the application until a mass market develops. Growth concentrates on marketing, commercialization, and other business aspects aiming for sustainable growth. In the maturation phase, applications, production processes, and business models are refined, commoditizing products. In the decline or renewal phase, the industry faces decline or is renewed through developing new technologies based on science, repeating the previous phases. Key transitions, such as the "Science & Technology" Transition, the "Technology & Application" Transition, and the "Application & Market" Transition, mark critical passages between scientific research, applied technology, and large-scale commercialization. The diagram also highlights the need for financial investments at each phase, essential for ensuring the continuity and success of each transition within the innovation cycle. The S&T&I cycle is a continuous and dynamic process involving multiple phases of development and transition, where financial and collaborative support among scientists, engineers, entrepreneurs, and public policies is essential to promoting an environment conducive to technological innovation and sustainable economic development.
Creating an Environment of Innovation and Collaboration
Finally, Dr. Marcelo proposed creating a modern and dynamic environment that fosters innovation from science, encouraging collaboration among scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs. He emphasized that this environment should promote the creation of startups and spin-offs from research activities, transforming Brazil's robust research base into a source of technological innovation and economic development. To boost GDP growth, it is crucial to invest strategically in R&D and human capital formation rather than merely allocating resources without planning. We must strengthen the capacities of governmental and private institutions, promoting intelligent investments and effective partnerships between the public and private sectors. This approach ensures that resources are used efficiently, promoting innovation and sustainable economic development.